Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
General Discussion
Related: Editorials & Other Articles, Issue Forums, Alliance Forums, Region Forums38 Years Ago Today; The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convention_on_the_Elimination_of_All_Forms_of_Discrimination_Against_Women
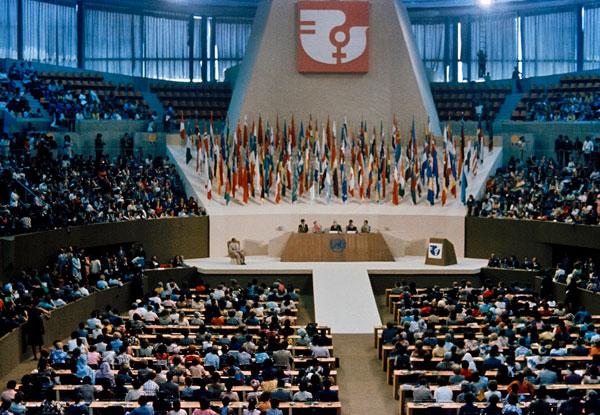

The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the Convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the Convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, Sudan, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.
The CEDAW Chairperson position is currently held by Hilary Gbedemah.
The Convention
Summary
The Convention has a similar format to the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, "both with regard to the scope of its substantive obligations and its international monitoring mechanisms". The Convention is structured in six parts with 30 articles total.
Part I (Articles 1-6) focuses on non-discrimination, sex stereotypes, and sex trafficking.
Part II (Articles 7-9) outlines women's rights in the public sphere with an emphasis on political life, representation, and rights to
nationality.
Part III (Articles 10-14) describes the economic and social rights of women, particularly focusing on education, employment, and health. Part III also includes special protections for rural women and the problems they face.
Part IV (Article 15 and 16) outlines women's right to equality in marriage and family life along with the right to equality before the law.
Part V (Articles 17-22) establishes the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women as well as the states parties' reporting procedure.
Part VI (Articles 23-30) describes the effects of the Convention on other treaties, the commitment of the states parties and the administration of the Convention.
Core Provisions
Article 1 defines discrimination against women in the following terms:
Any distinction, exclusion or restriction made on the basis of sex which has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise by women, irrespective of their marital status, on a basis of equality of men and women, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field.
Article 2 mandates that states parties ratifying the Convention declare intent to enshrine gender equality into their domestic legislation, repeal all discriminatory provisions in their laws, and enact new provisions to guard against discrimination against women. States ratifying the Convention must also establish tribunals and public institutions to guarantee women effective protection against discrimination, and take steps to eliminate all forms of discrimination practiced against women by individuals, organizations, and enterprises.
Article 3 requires states parties to guarantee basic human rights and fundamental freedoms to women "on a basis of equality with men" through the "political, social, economic, and cultural fields."
Article 4 notes that "[a]doption...of special measures aimed at accelerating de facto equality between men and women shall not be considered discrimination." It adds that special protection for maternity is not regarded as gender discrimination.
Article 5 requires states parties to take measures to seek to eliminate prejudices and customs based on the idea of the inferiority or the superiority of one sex or on stereotyped role for men and women. It also mandates the states parties "[t]o ensure...the recognition of the common responsibility of men and women in the upbringing and development of their children."
Article 6 obliges states parties to "take all appropriate measures, including legislation, to suppress all forms of trafficking in women and exploitation of prostitution of women."
Article 7 guarantees women equality in political and public life with a focus on equality in voting, participation in government, and participation in "non-governmental organizations and associations concerned with the public and political life of the country."
Article 8 provides that states parties will guarantee women's equal "opportunity to represent their Government at the international level and to participate in the work of international organizations."
Article 9 mandates state parties to "grant women equal rights with men to acquire, change or retain their nationality" and equal rights "with respect to the nationality of their children."
Article 10 necessitates equal opportunity in education for female students and encourages coeducation. It also provides equal access to athletics, scholarships and grants as well as requires "reduction in female students' drop out rates."
Article 11 outlines the right to work for women as "an unalienable right of all human beings." It requires equal pay for equal work, the right to social security, paid leave and maternity leave "with pay or with comparable social benefits without loss of former employment, seniority or social allowances." Dismissal on the grounds of maternity, pregnancy or status of marriage shall be prohibited with sanction.
Article 12 creates the obligation of states parties to "take all appropriate measures to eliminate discrimination against women in the field of healthcare in order to ensure...access to health care services, including those related to family planning."
Article 13 guarantees equality to women "in economic and social life," especially with respect to "the right to family benefits, the right to bank loans, mortgages and other forms of financial credit, and the right to participate in recreational activities, sports and all aspects of cultural life."
Article 14 provides protections for rural women and their special problems, ensuring the right of women to participate in development programs, "to have access to adequate health care facilities," "to participate in all community activities," "to have access to agricultural credit" and "to enjoy adequate living conditions."
Article 15 obliges states parties to guarantee "women equality with men before the law," including "a legal capacity identical to that of men." It also accords "to men and women the same rights with regard to the law relating to the movement of persons and the freedom to choose their residence and domicile."
Article 16 prohibits "discrimination against women in all matters relating to marriage and family relations." In particular, it provides men and women with "the same right to enter into marriage, the same right freely to choose a spouse," "the same rights and responsibilities during marriage and at its dissolution," "the same rights and responsibilities as parents," "the same rights to decide freely and responsibly on the number and spacing of their children," "the same personal rights as husband and wife, including the right to choose a family name, a profession and an occupation" "the same rights for both spouses in respect of the ownership, acquisition, management, administration, enjoyment and disposition of property, whether free of charge or for a valuable consideration."
Articles 17 - 24 These articles describe the composition and procedures of the CEDAW Committee,like the hierarchical structure and rules and regulations of systematic procedure of the relationship between CEDAW and national and international legislation and the obligation of States to take all steps necessary to implement CEDAW in full form.
Articles 25 - 30 (Administration of CEDAW)
These articles describe the general administrative procedures concerning enforcement of CEDAW, ratification and entering reservations of concerned states.
</snip>

The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the Convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the Convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, Sudan, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.
The CEDAW Chairperson position is currently held by Hilary Gbedemah.
The Convention
Summary
The Convention has a similar format to the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination, "both with regard to the scope of its substantive obligations and its international monitoring mechanisms". The Convention is structured in six parts with 30 articles total.
Part I (Articles 1-6) focuses on non-discrimination, sex stereotypes, and sex trafficking.
Part II (Articles 7-9) outlines women's rights in the public sphere with an emphasis on political life, representation, and rights to
nationality.
Part III (Articles 10-14) describes the economic and social rights of women, particularly focusing on education, employment, and health. Part III also includes special protections for rural women and the problems they face.
Part IV (Article 15 and 16) outlines women's right to equality in marriage and family life along with the right to equality before the law.
Part V (Articles 17-22) establishes the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women as well as the states parties' reporting procedure.
Part VI (Articles 23-30) describes the effects of the Convention on other treaties, the commitment of the states parties and the administration of the Convention.
Core Provisions
Article 1 defines discrimination against women in the following terms:
Any distinction, exclusion or restriction made on the basis of sex which has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise by women, irrespective of their marital status, on a basis of equality of men and women, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field.
Article 2 mandates that states parties ratifying the Convention declare intent to enshrine gender equality into their domestic legislation, repeal all discriminatory provisions in their laws, and enact new provisions to guard against discrimination against women. States ratifying the Convention must also establish tribunals and public institutions to guarantee women effective protection against discrimination, and take steps to eliminate all forms of discrimination practiced against women by individuals, organizations, and enterprises.
Article 3 requires states parties to guarantee basic human rights and fundamental freedoms to women "on a basis of equality with men" through the "political, social, economic, and cultural fields."
Article 4 notes that "[a]doption...of special measures aimed at accelerating de facto equality between men and women shall not be considered discrimination." It adds that special protection for maternity is not regarded as gender discrimination.
Article 5 requires states parties to take measures to seek to eliminate prejudices and customs based on the idea of the inferiority or the superiority of one sex or on stereotyped role for men and women. It also mandates the states parties "[t]o ensure...the recognition of the common responsibility of men and women in the upbringing and development of their children."
Article 6 obliges states parties to "take all appropriate measures, including legislation, to suppress all forms of trafficking in women and exploitation of prostitution of women."
Article 7 guarantees women equality in political and public life with a focus on equality in voting, participation in government, and participation in "non-governmental organizations and associations concerned with the public and political life of the country."
Article 8 provides that states parties will guarantee women's equal "opportunity to represent their Government at the international level and to participate in the work of international organizations."
Article 9 mandates state parties to "grant women equal rights with men to acquire, change or retain their nationality" and equal rights "with respect to the nationality of their children."
Article 10 necessitates equal opportunity in education for female students and encourages coeducation. It also provides equal access to athletics, scholarships and grants as well as requires "reduction in female students' drop out rates."
Article 11 outlines the right to work for women as "an unalienable right of all human beings." It requires equal pay for equal work, the right to social security, paid leave and maternity leave "with pay or with comparable social benefits without loss of former employment, seniority or social allowances." Dismissal on the grounds of maternity, pregnancy or status of marriage shall be prohibited with sanction.
Article 12 creates the obligation of states parties to "take all appropriate measures to eliminate discrimination against women in the field of healthcare in order to ensure...access to health care services, including those related to family planning."
Article 13 guarantees equality to women "in economic and social life," especially with respect to "the right to family benefits, the right to bank loans, mortgages and other forms of financial credit, and the right to participate in recreational activities, sports and all aspects of cultural life."
Article 14 provides protections for rural women and their special problems, ensuring the right of women to participate in development programs, "to have access to adequate health care facilities," "to participate in all community activities," "to have access to agricultural credit" and "to enjoy adequate living conditions."
Article 15 obliges states parties to guarantee "women equality with men before the law," including "a legal capacity identical to that of men." It also accords "to men and women the same rights with regard to the law relating to the movement of persons and the freedom to choose their residence and domicile."
Article 16 prohibits "discrimination against women in all matters relating to marriage and family relations." In particular, it provides men and women with "the same right to enter into marriage, the same right freely to choose a spouse," "the same rights and responsibilities during marriage and at its dissolution," "the same rights and responsibilities as parents," "the same rights to decide freely and responsibly on the number and spacing of their children," "the same personal rights as husband and wife, including the right to choose a family name, a profession and an occupation" "the same rights for both spouses in respect of the ownership, acquisition, management, administration, enjoyment and disposition of property, whether free of charge or for a valuable consideration."
Articles 17 - 24 These articles describe the composition and procedures of the CEDAW Committee,like the hierarchical structure and rules and regulations of systematic procedure of the relationship between CEDAW and national and international legislation and the obligation of States to take all steps necessary to implement CEDAW in full form.
Articles 25 - 30 (Administration of CEDAW)
These articles describe the general administrative procedures concerning enforcement of CEDAW, ratification and entering reservations of concerned states.
</snip>
InfoView thread info, including edit history
TrashPut this thread in your Trash Can (My DU » Trash Can)
BookmarkAdd this thread to your Bookmarks (My DU » Bookmarks)
1 replies, 631 views
ShareGet links to this post and/or share on social media
AlertAlert this post for a rule violation
PowersThere are no powers you can use on this post
EditCannot edit other people's posts
ReplyReply to this post
EditCannot edit other people's posts
Rec (5)
ReplyReply to this post
1 replies
 = new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
= new reply since forum marked as read
Highlight:
NoneDon't highlight anything
5 newestHighlight 5 most recent replies
38 Years Ago Today; The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (Original Post)
Dennis Donovan
Sep 2019
OP
Niagara
(7,595 posts)1. Kicking