Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
Editorials & Other Articles
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
General Discussion
Related: Editorials & Other Articles, Issue Forums, Alliance Forums, Region ForumsWith so much attention on #COVID19 in children, time for an updated #tweetorial on what we do and
don't know!Alasdair Munro
@apsmunro
Paediatric registrar | Clinical Research Fellow Paeds ID
https://twitter.com/southamptonCRF
@southamptonCRF
|
@DFTBubbles
#COVID19 review lead | Origami and Nando's | Husband and dad
Joined April 2013
Research interests: Paediatric infectious diseases, Biofilms, Antimicrobial Resistance, Sepsis, Bacteraemia
https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=2zPIy8cAAAAJ&hl=en
https://threadreaderapp.com/thread/1263493025650614279.html
We'll talk impact, risk, hyperinflammation syndrome, transmission, schools and more
Lets go!
1/21
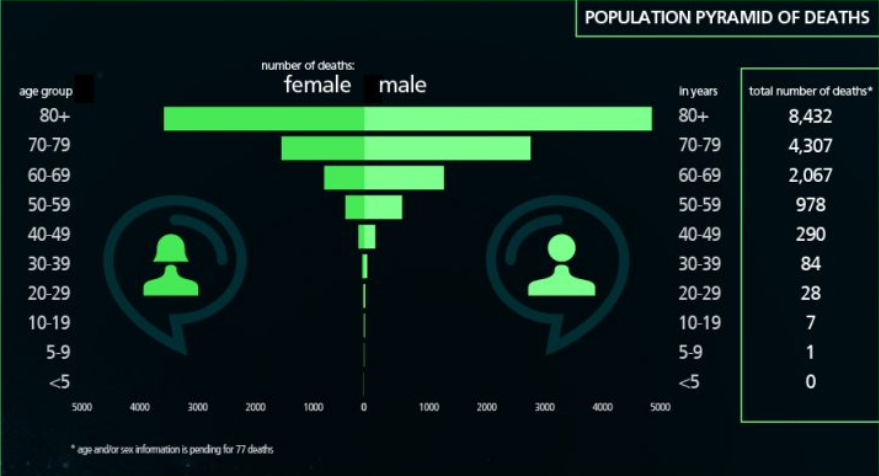
Children remain grossly underrepresented in all case numbers, hospital admissions and deaths worldwide
See latest ISARIC report of >15,000 severe cases, or @PHE_uk UK deaths
https://media.tghn.org/medialibrary/2020/05/ISARIC_Data_Platform_COVID-19_Report_6MAY20.pdf
https://publichealthmatters.blog.gov.uk/2020/04/23/coronavirus-covid-19-using-data-to-track-the-virus/
2/21
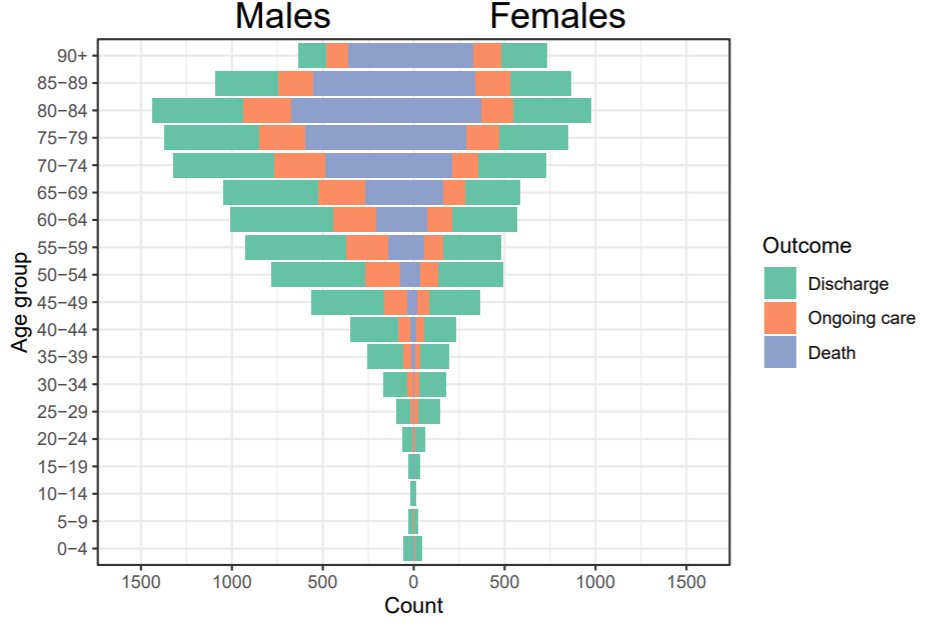
This report from @sunilbhop and friends looks at child deaths from #COVID19 compared to other causes to put them in perspective
Of ~37,000 child deaths, 43 were from COVID19
In the words of @d_spiegel , children are "unbelievably low risk"
3/21
Link to tweet
https://threadreaderapp.com/thread/1262315964898697217.html
Are some children higher risk?
Small numbers, but children usually at risk from viral respiratory infections look equally at risk from #COVID19, including tech dependent, neurodisability, malignancy or chronic lung disease
Outcomes of Children With COVID-19 Admitted to US and Canadian Pediatric Intensive Care Units
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2766037
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Hospitalized and Critically Ill Children and Adolescents with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) at a Tertiary Care Medical Center in New York City
To describe the clinical profiles and risk factors for critical illness in hospitalized children and adolescents with COVID-19.
https://tinyurl.com/yaudwm9c
4/21
Important to note outcomes still pretty good for these groups, and there a number of documented cases for some (e.g. oncology, immunosuppressed) which had a predominantly mild clinical course
Even most of these children don't get very sick
COVID-19 in Children With Cancer in New York City
This cross-sectional study assesses the risk associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 for pediatric patients with cancer.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2766112
5/21
What about this hyperinflammatory syndrome?
It's called PIMS-TS (or MIS-C in the USA)
It seems to be an immune reaction after COVID19 infection (approx 2 - 4 weeks)
Usually starts with persistent fever, abdo pain and D&V, then can present similar to Kawasakis (+/- shock)
6/21
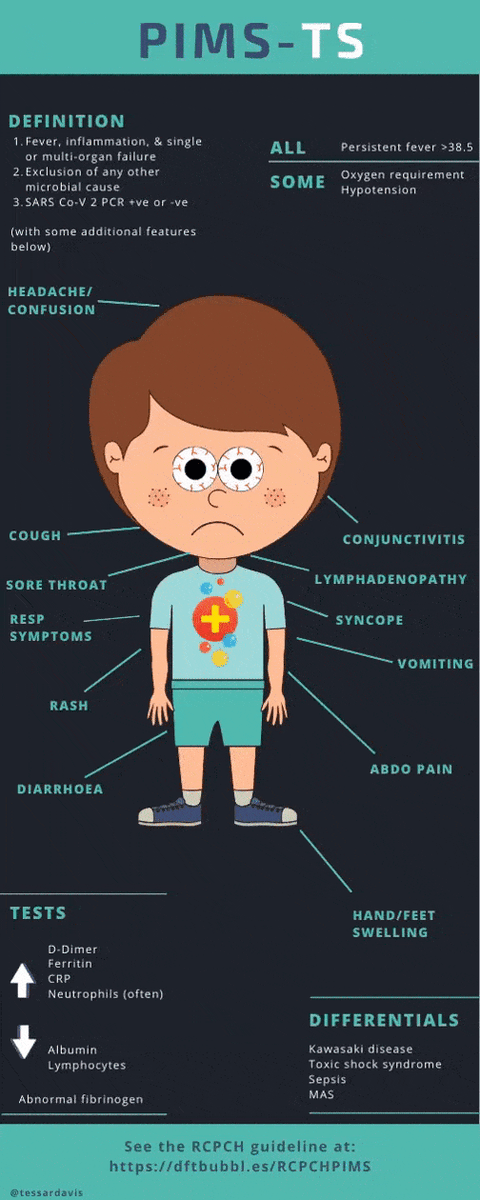
We currently have 3 published cohorts from London, Italy and France
Many kids get very sick, but most recover well
It seems to be dissipating (following trends in peaks of infection)
Read more about it here
Paediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome
It has become increasingly clear that children are less frequently affected by severe COVID-19 than adults.
https://dontforgetthebubbles.com/pims-ts/
7/21
It can be serious, but is incredibly rare
In Europe there have been about 230 cases and very few deaths. There are >80 million children
Europe CDC considers it a low risk. Be reassured
https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/covid-19-risk-assessment-paediatric-inflammatory-multisystem-syndrome-15-May-2020.pdf
8/21
OK - transmission. Let's go step by step.
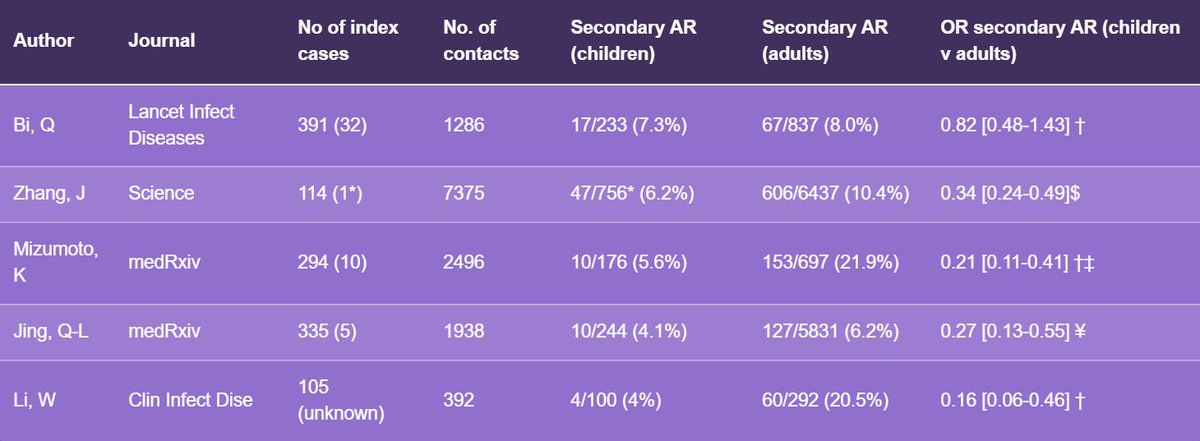
How easily to children catch it?
5 studies have looked at transmission to children (mainly household) and 4/5 found *significantly lower* attack rates in children than adults
The missing link? Children and transmission of SARS-CoV-2
https://dontforgetthebubbles.com/the-missing-link-children-and-transmission-of-sars-cov-2/
9/21
How many children actually have/had COVID19?
<2% of known cases have been in children, but given symptoms are so mild have we just missed them all? Are they mainly asymptomatic? Are they silent assassins?
This is harder to tell, but there is some evidence...
10/21
Iceland tested those at risk and found 1/2 rate of infection in children <10y compared to adults, and 0 cases in asymptomatic screening
Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the Icelandic Population | NEJM
Original Article from The New England Journal of Medicine — Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the Icelandic Population
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2006100
Vo, Italy screened >85% of the population. 2.6% had COVID19, but 0 children <10y
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.17.20053157v1
11/21
Some say ONS data shows there's no difference between children and adult infection rates
But they found ~30 positive cases in 10,000 people
The CIs are too wide for inference about relative infection rates (compatible with 10x rates in any group)
https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/conditionsanddiseases/bulletins/coronaviruscovid19infectionsurveypilot/england14may2020?WT.mc_id=9e5557c21c93a6f19d36bf985082f4de&WT.sn_type=TWITTER&hoot.message=There%20is%20currently%20no%20evidence%20that%20age%20affects%20the%20likelihood%20of%20being%20infected%20with%20COVID-19%20%5BLINK%5D&hoot.send_date=2020-05-14%2013%3A15%3A14&hoot.username=ONS&hoot.send_dayofweek=Thursday&hoot.send_hour=13&hootPostID=602e6bfaca6d5de6b869e70e6e9a7230#main-points
12/21
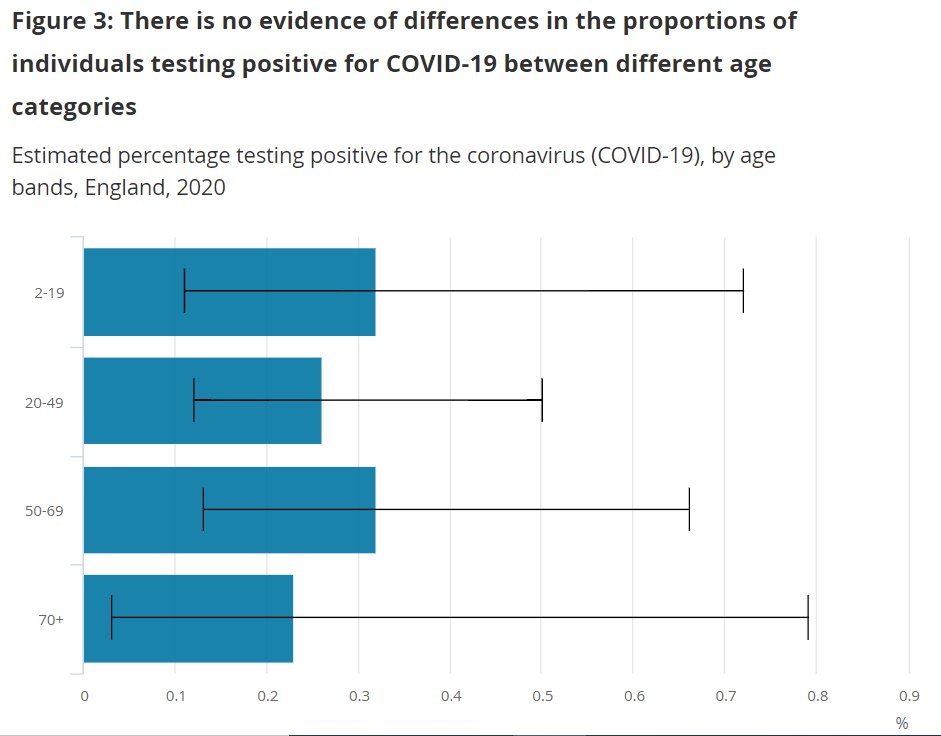
The same principle applies for 2 sero-epi studies from Switzerland & Germany
Despite lower rates of infection in children, numbers too small to be statistically significant
This is not evidence for equal rates of infection
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.02.20088898v1
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.04.20090076v1
13/21
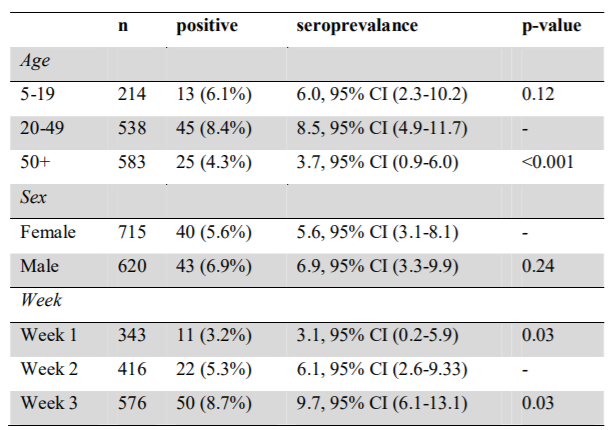
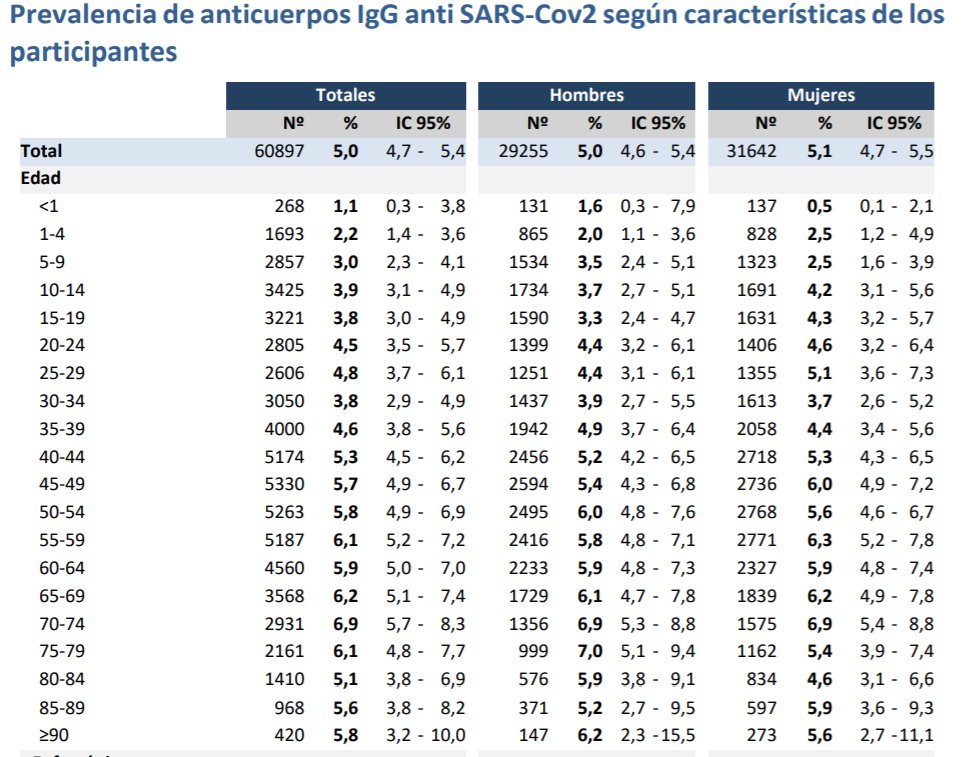
What do we find if we do proper sized sero-epi?
Infection rates of 1-3% in children compared to 5% in adults in a Spanish study of >60,000 people
https://www.ciencia.gob.es/stfls/MICINN/Ministerio/FICHEROS/ENECOVID_Informe_preliminar_cierre_primera_ronda_13Mayo2020.pdf
14/21
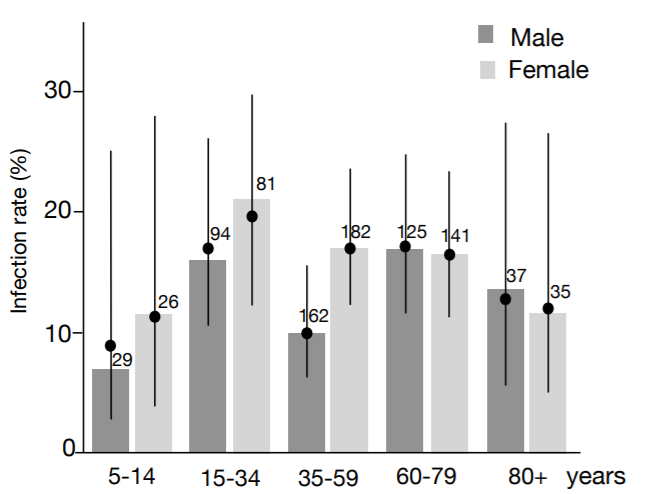
How infectious are children when infected?
Hard to say. Some examples of children not spreading at all despite multiple exposures (>100 other children) but spreading other respiratory viruses
Cluster of coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) in the French Alps, 2020
Abstract Background. On 07/02/2020, French Health authorities were informed of a confirmed case of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus in an Englishman infected in Singapore
https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa424/5819060
15/21
A German study claimed to find similar viral loads in children as adults, stating they're "just as infectious"
https://zoonosen.charite.de/fileadmin/user_upload/microsites/m_cc05/virologie-ccm/dateien_upload/Weitere_Dateien/analysis-of-SARS-CoV-2-viral-load-by-patient-age.pdf
Amongst other issues, if analysed properly the data actually showed significantly lower viral loads in children
https://osf.io/bkuar/
16/21
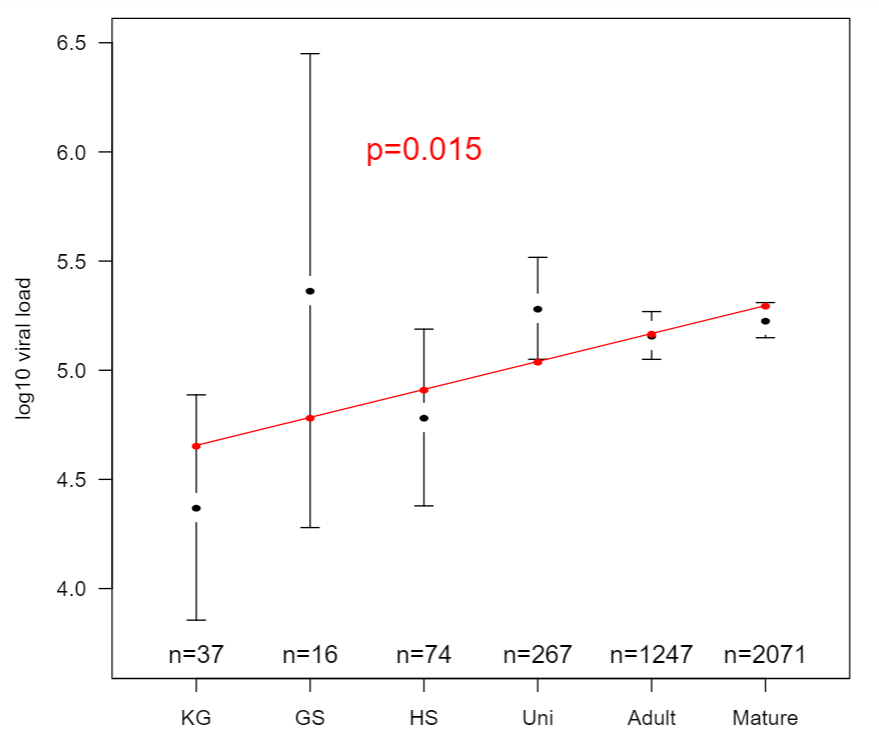
National reports from Netherlands
https://www.rivm.nl/en/novel-coronavirus-covid-19/children-and-covid-19
Iceland
https://www.eapaediatrics.eu/eap-blog-covid-19-series-5-icelands-data-on-the-infectivity-of-children-cross-infection-risk/
Norway
https://www.fhi.no/contentassets/c9e459cd7cc24991810a0d28d7803bd0/notat-om-risiko-og-respons-2020-05-05.pdf
Australia
http://ncirs.org.au/sites/default/files/2020-04/NCIRS%20NSW%20Schools%20COVID_Summary_FINAL%20public_26%20April%202020.pdf
Have found limited evidence of children contributing to spread of COVID19. Most transmission is adult to adult.
17/21

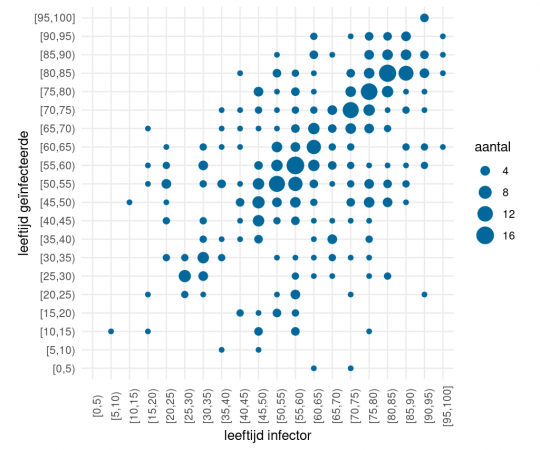
What does it mean for schools?
Children are not COVID-19 super spreaders: time to go back to school
https://adc.bmj.com/content/early/2020/05/19/archdischild-2020-319474
Children can get COVID19 so can almost certainly spread it
But, they are barely affected by infection, and appear less likely to catch or spread it than adults
Schools seem lower risk than adult work environments
18/21
Will outbreaks happen? Of course.
But this is our new reality for the foreseeable future. We need to mitigate against the risks and ensure mechanisms for quick response (track/trace/isolate) are in place
Children suffer harm from lockdown
https://bmjpaedsopen.bmj.com/content/4/1/e000701
19/21
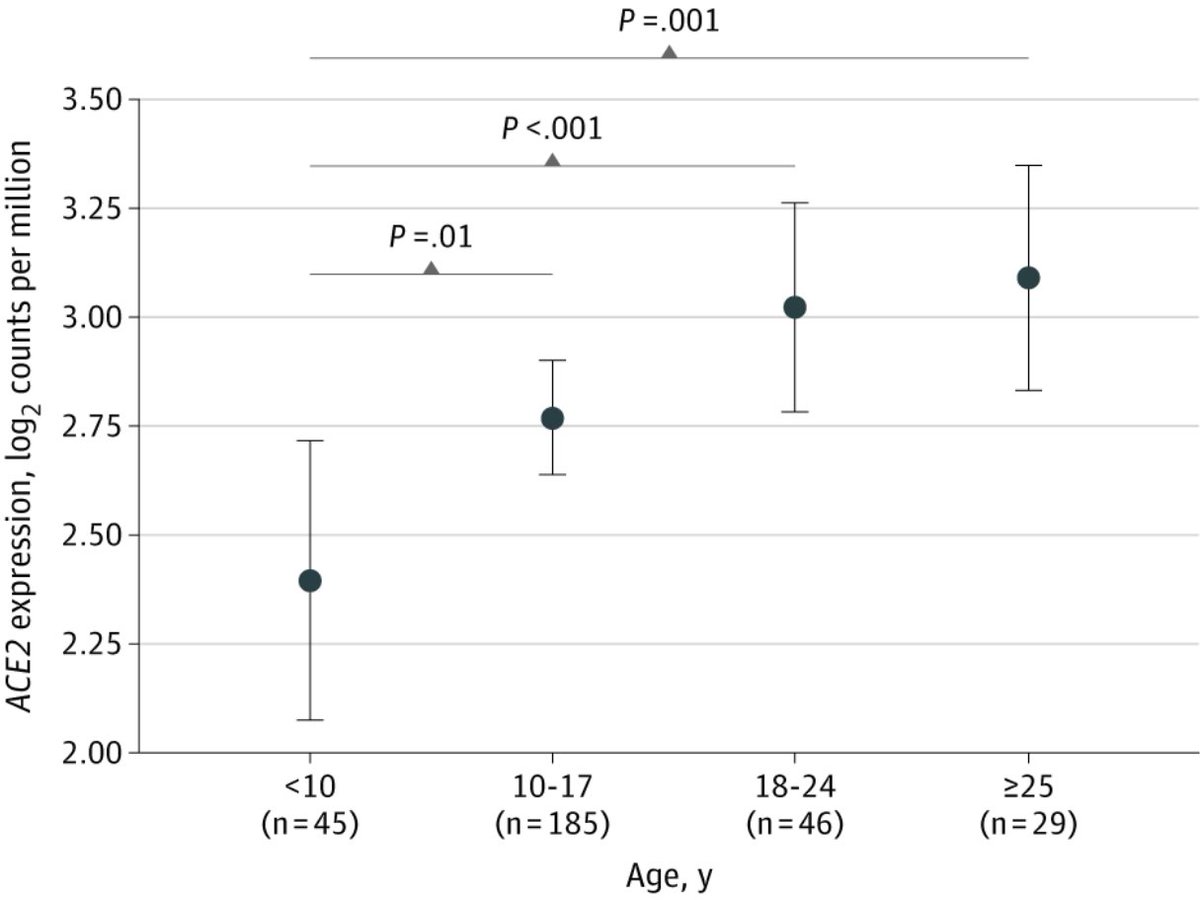
Now for WHY children seem so much less affected...
Still no clear answers. Possible differences in ACE2 expression, but they seem small
Nasal Gene Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Children and Adults
This study compares angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) gene expression, which has been associated with SARS-CoV-2 cell entry, in the nasal epithelium of children vs adults.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2766524?utm_source=twitter&utm_campaign=content-shareicons&utm_content=article_engagement&utm_medium=social&utm_term=052020#.XsVklEVpvmF.twitter
Some suggest immune differences. Need to be proven.
The immune system of children: the key to understanding SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility?
https://tinyurl.com/ybzfdfuq
More research needed...!
20/21
Thanks for making it to the end!
For our comprehensive review of all paediatric #COVID19 literature (cited by @UKRI_News and @WHO ) check it out here on @DFTBubbles
21/21
AN EVIDENCE SUMMARY OF PAEDIATRIC COVID-19 LITERATURE
https://dontforgetthebubbles.com/evidence-summary-paediatric-covid-19-literature/